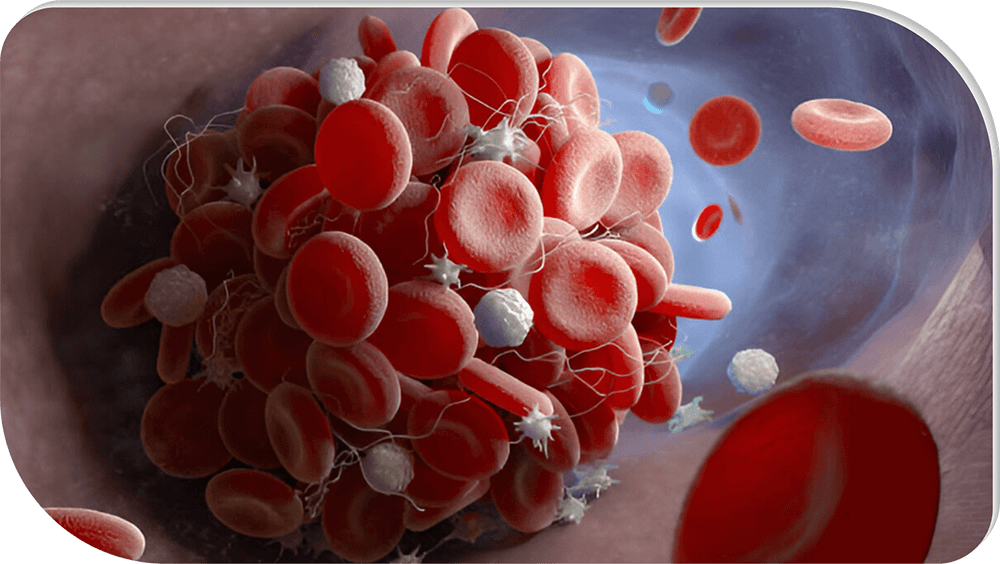
Platelets are essential for hemostasis and thrombus formation. Platelet aggregation plays a key role in arterial ischemic events like coronary artery disease, strokes, and peripheral artery disease, making antiplatelet therapy vital for preventing recurrence in affected individuals.
Despite treatment, up to 50% of patients experience recurrent strokes and vascular events, partly due to resistance to standard antiplatelet therapy. Resistance has been observed in up to 65% of aspirin users, 56% with clopidogrel, and 35% with the combination. Contributing factors include slow pharmacodynamics, pharmacogenetic variations, high baseline platelet activity, inadequate dosing, and poor compliance. A key challenge is that many patients remain at risk for thrombosis or life-threatening bleeding.
A comprehensive antiplatelet therapy should include the following clinically proven features:
- Standalone antiplatelet efficacy
- Enhances the effectiveness of standard antiplatelet and antidyslipidemic therapies.
- Antiplatelet effectiveness in therapy-resistant cases.
- Improves metabolic health, including lipid and glucose levels.
- Long term efficacy and safety